Nursing malpractice and nursing negligence are quite similar, but very different. The distinction is important for nurses to know and understand. Let’s define and give examples of both, plus go through some FAQs that will help you truly understand the difference between nursing malpractice and nursing negligence.
Nursing Malpractice vs. Nursing Negligence
Before we can really dig into the difference between malpractice and negligence, we need to have a baseline understanding of our standard of practice as nurses.
A Nursing Standard of Care Violation
A nursing standard of care violation occurs when a nurse fails to provide care that meets the accepted standards of nursing practice. The nursing standard of care refers to the level of care that a reasonably prudent nurse would provide under similar circumstances. Nurses are held to a high standard of care, and when they fail to meet this standard, they can be held liable for any harm that results.
Examples of nursing standard of care violations are below.
Medication Errors
Nurses must ensure that medications are administered correctly and at the appropriate time. A medication error can occur if a nurse administers the wrong medication, the wrong dose, at the wrong time, to the wrong patient, via the wrong route, or prepared improperly (for example, giving IV medications in one line that are not compatible with one another).
Failure to Monitor
Nurses are responsible for monitoring patients’ hemodynamics, assessments and other indicators of health as ordered by the physician and as outlined by the healthcare organization’s policies and procedures. Failure to properly monitor a patient’s condition can result in serious harm or even death.
Infection Control
Nurses must take appropriate measures to prevent the spread of infection. Failure to follow infection control protocols can result in the spread of infectious diseases.
Failure to Communicate
Nurses must communicate effectively with other healthcare providers, including doctors, other nurses, and support staff. Failure to communicate can result in misdiagnosis, delayed treatment, or other adverse outcomes.
Patient Falls and Injuries
Nurses must take steps to prevent patient falls, including monitoring patients who are at risk of falling and ensuring that patients have appropriate assistive devices.
These are just a few examples of nursing standard of care violations. When a nurse violates the nursing standard of care and a patient is harmed as a result, the nurse may be held liable for malpractice.
What Is Nursing Negligence?
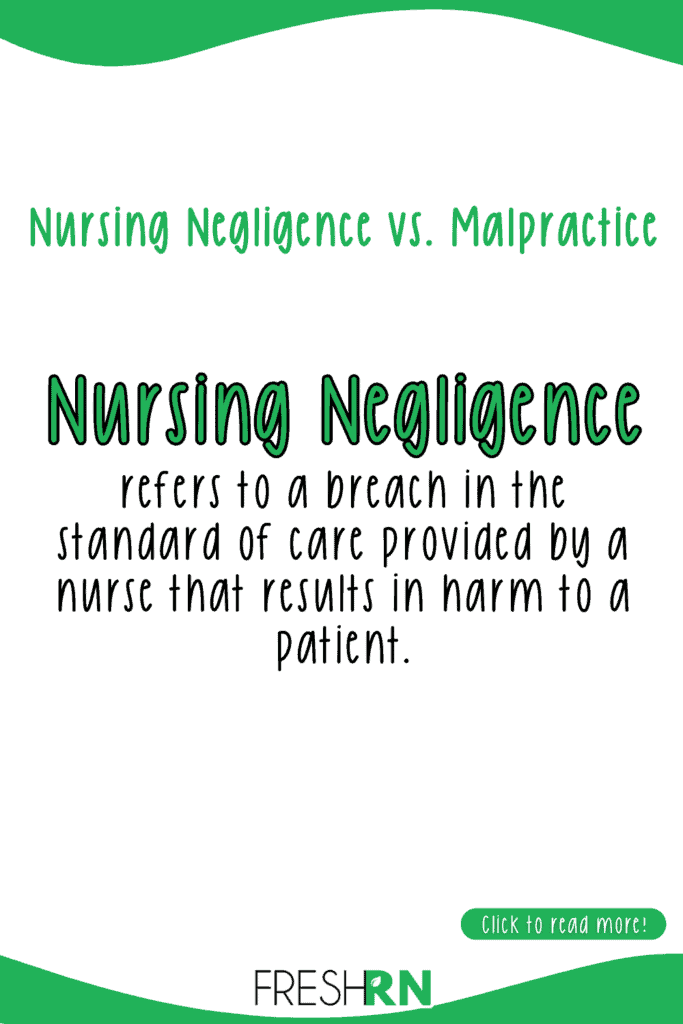
Nursing negligence refers to a breach in the standard of care provided by a nurse that results in harm to a patient.
An example of medical negligence would be if a nurse failed to properly monitor a patient’s vital signs and as a result, the patient goes into cardiac arrest. Even if the nurse followed all of the standards of care procedures, if they were not monitoring the patient’s vitals closely enough they could be considered negligent.
10 Examples of Nursing Negligence
- Failing to properly assess a patient’s condition, leading to a delay in treatment.
- Failing to report significant changes in a patient’s condition to the physician or other members of the healthcare team.
- Failing to follow a physician’s orders or treatment plan.
- Failing to properly supervise nursing assistants or other staff members.
- Failing to provide adequate education or instruction to a patient or family member regarding care instructions, medications, or self-care management.
- Failing to properly document a patient’s care or medication administration.
- Failing to properly use and maintain medical equipment, leading to injury or harm to a patient.
- Failing to follow infection control protocols, leading to the spread of infectious diseases.
- Failing to provide adequate pain management or symptom relief to a patient.
- Failing to advocate for a patient’s needs or rights, such as ensuring informed consent or addressing concerns with the healthcare team.
What is Nursing Malpractice?

Nursing malpractice is a type of negligence in which a nurse fails to provide the expected standard of care, resulting in harm to the patient. This means that even if the care they provided was not negligent, it would still be considered nursing malpractice if they failed to meet any one of the nursing standards of care.
10 Examples of Nursing Malpractice
- Failing to turn or reposition a patient, leading to pressure ulcers.
- Failing to provide adequate nutrition or hydration, leading to malnutrition or dehydration.
- Failing to respond to a patient’s call light or request for assistance in a timely manner leading to injury or delayed treatment.
- Administering the wrong medication or dosage, leading to adverse reactions or harm.
- Failing to properly document a patient’s care, including vital signs, medication administration, and changes in condition.
- Failing to properly clean and dress a wound, leading to infection or delayed healing.
- Failing to properly monitor a patient’s condition, leading to delayed diagnosis or treatment.
- Failing to properly administer or monitor the use of medical equipment, such as ventilators or feeding tubes.
- Failing to follow infection control protocols, leading to the spread of infectious diseases.
- Failing to provide appropriate patient education or discharge instructions, leading to poor health outcomes or readmission to the hospital.
Getting ready for nursing school clinicals, but feeling unprepared?

Nursing Skills Refresh from FreshRN is a self-paced video course for both new and experienced nurses. Whether you’re preparing for your first clinical experience, or need to brush up on your nursing skills, this course is for you. Each lesson walks you through the basic tasks and concepts you will experience in the clinical setting. Once completed, you’ll feel comfortable in a hospital setting, understand the basics of what the bedside experience will feel like, and know insider tips and tricks that will make you feel confident and in control.
Nursing Malpractice vs. Nursing Negligence
Negligence is very similar to medical malpractice, but there are three key differences.
- Negligence does not require that the healthcare professional violate any standards of care.
- Only injuries caused by negligence will be sufficient in a claim for damages against the healthcare professional. An injury must be proven to have had a substantial effect on someone’s life before it qualifies as the basis for a claim of negligent behavior.
- Unlike malpractice, negligence doesn’t necessarily occur with bad intentions; it can also occur simply through unintentional mistakes or omissions.
I hope this helps makes some sense between these two similar, yet very different serious situations. If something happened and you’re worried, I recommend speaking with a lawyer to understand implications.
Frequently Asked Questions About Nursing Malpractice vs. Nursing Negligence
More Resources
- Common Questions About Malpractice Insurance for Nurses
- Deep Dive: RaDonda Vaught Trial, Charges, and Timeline
- RaDonda Vaught Part 2: An Interview With a Nurse Attorney
Worried you’ll look clueless at clinicals? We’ve got you.

Nursing clinicals are awkward at first. You’re surrounded by experienced nurses, real patients, and you’re just trying to figure out where the gloves are. It’s a lot.
That’s why we created Nursing Skills Refresh—to give you a realistic, supportive head start. You’ll get demo videos of common procedures, insider tips from two experienced nurses, and a clear picture of how a shift actually flows. (and a lot more) The goal? Walk into clinicals feeling like you belong there—not like you’re in the way.
Start Lesson #1 Now



0 Comments